What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (Full form of PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It involves a combination of symptoms and underlying health issues that can impact a woman’s menstrual cycle, fertility, appearance, and overall health.
All about PCOS
What Causes PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS isn’t fully understood, but several factors are known to play a role:
Hormonal Imbalance: Women with PCOS often have higher levels of androgens, which are male hormones present in small amounts in all women. This imbalance can disrupt the normal function of the ovaries, leading to issues like irregular periods, excess hair growth, and acne.
Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, meaning their body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin. This can lead to elevated insulin levels, which may increase androgen production, contributing to the symptoms of PCOS.
Genetics: PCOS often runs in families. If your mother or sister has PCOS, your chances of having it may be higher, indicating a genetic predisposition.
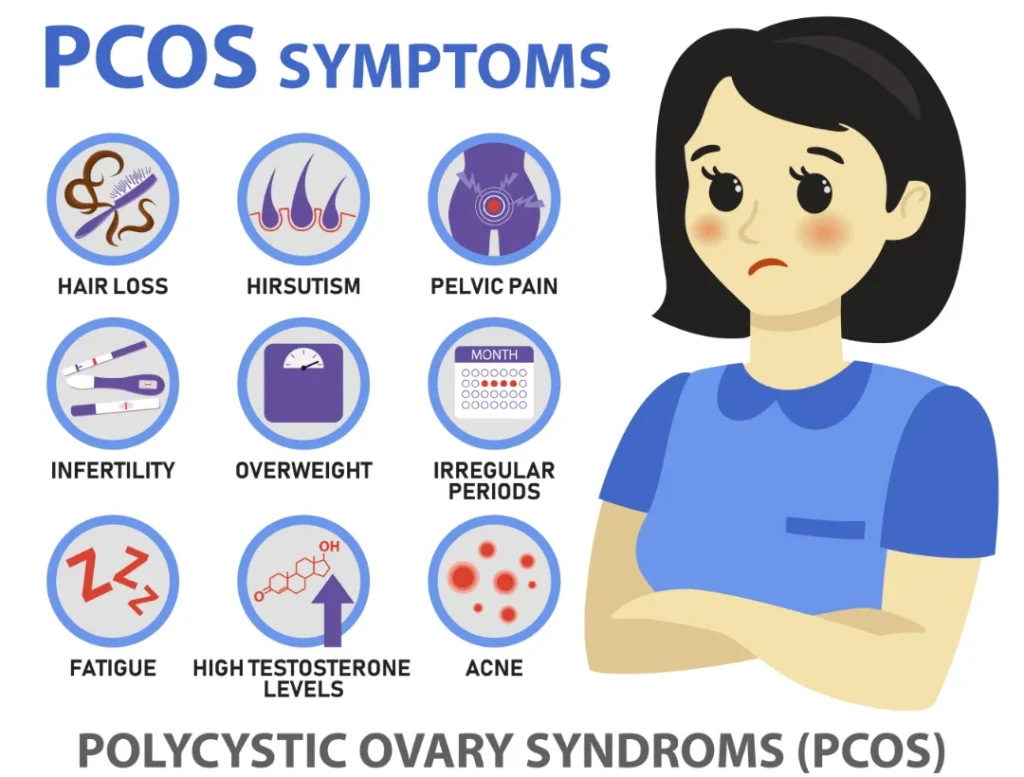
Key Symptoms of PCOS
Irregular Periods: Women with PCOS frequently experience infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles. Some may have fewer than nine periods a year, or very heavy periods.

Excess Hair Growth: Known as hirsutism, this symptom includes increased hair growth on the face, chest, back, or other areas typically associated with male-pattern hair growth.
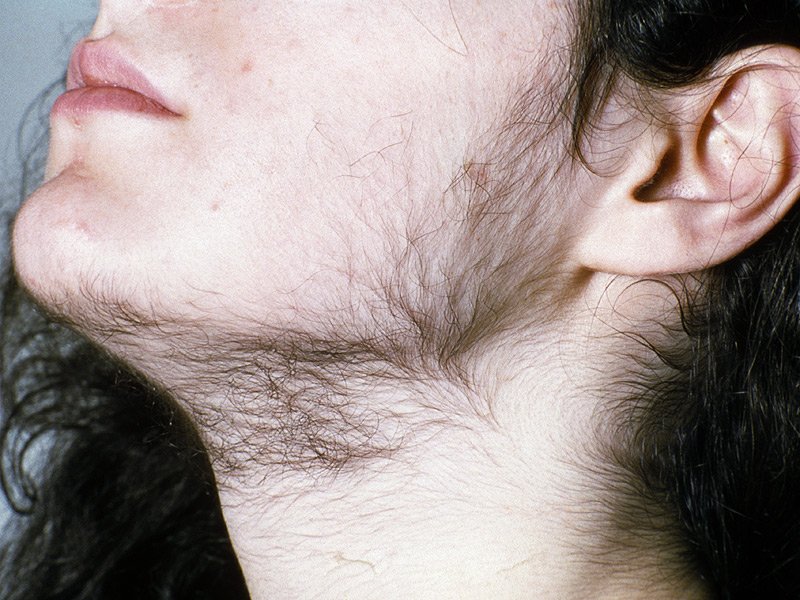
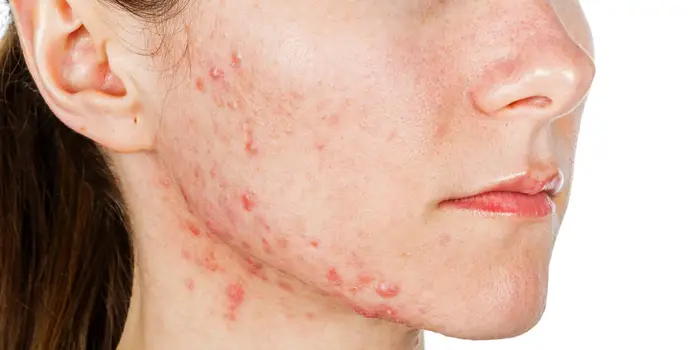
Acne and Oily Skin: Higher levels of androgens can lead to skin issues like acne, especially on the face, chest, and upper back.
Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS struggle with weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, and find it difficult to lose weight.

Thinning Hair: Hair thinning on the scalp, similar to male-pattern baldness, can occur.
Ovarian Cysts: The name “polycystic ovary syndrome” comes from the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, often visible on ultrasound, although not all women with PCOS will have these cysts.
Basic Pathology of PCOS
- PCOS is characterized by a complex interaction between various hormonal and metabolic pathways:
- Increased Androgen Levels: The ovaries produce an excess of androgens, leading to symptoms such as hirsutism, acne, and irregular ovulation. Elevated androgens can interfere with the development of follicles in the ovaries, preventing normal ovulation.
- Follicular Development: Normally, follicles in the ovaries mature and release an egg during ovulation. In PCOS, due to hormonal imbalances, many follicles begin to mature, but they do not fully develop, resulting in the accumulation of immature follicles or “cysts” in the ovaries.
- Insulin Resistance: High insulin levels promote increased production of androgens in the ovaries, which exacerbates the hormonal imbalance. Insulin resistance is also linked to obesity and metabolic issues, which are common in PCOS.
- Inflammation: Low-grade inflammation is often present in women with PCOS. This inflammation may contribute to increased androgen levels, further complicating the condition.
Managing PCOS
While there is no cure for PCOS, symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes and medical treatments. One of the most effective ways to manage PCOS is through weight management:
Weight Loss and PCOS: Losing weight, even a small amount (5-10% of body weight), can significantly improve symptoms of PCOS. Weight loss can help lower insulin levels, reduce androgen levels, and restore normal menstrual cycles. It can also improve fertility and reduce the risk of long-term complications like type 2 diabetes and heart disease. A healthy diet and regular exercise are key components of a successful weight management plan.

Healthy Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables can help manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, is also important for managing weight and reducing symptoms.

Medications: Depending on your symptoms, your doctor might prescribe hormonal contraceptives to regulate menstrual cycles, anti-androgens to reduce hair growth and acne, or medications to improve insulin sensitivity.
Stress Management:Activities like yoga, meditation, and other relaxation techniques can help manage stress, which can influence hormone levels and symptoms.
Why is it Important to Manage PCOS?
Effective management of PCOS is crucial to prevent long-term health complications, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, and fertility issues. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve symptoms and reduce the risk of developing these complications.
Conclusion
PCOS is a complex condition that affects many aspects of a woman’s health, but with the right management strategies, its impact can be minimized. If you suspect you have PCOS or are experiencing any related symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan or need any help contact our Doctors at Health Authentica.










2 thoughts on “PCOS: The Rising Health Challenge for Girls and Women”