Introduction
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. It produces hormones that influence metabolism, energy levels, and overall health. Understanding thyroid health is essential for maintaining balance in your body and preventing potential disorders.
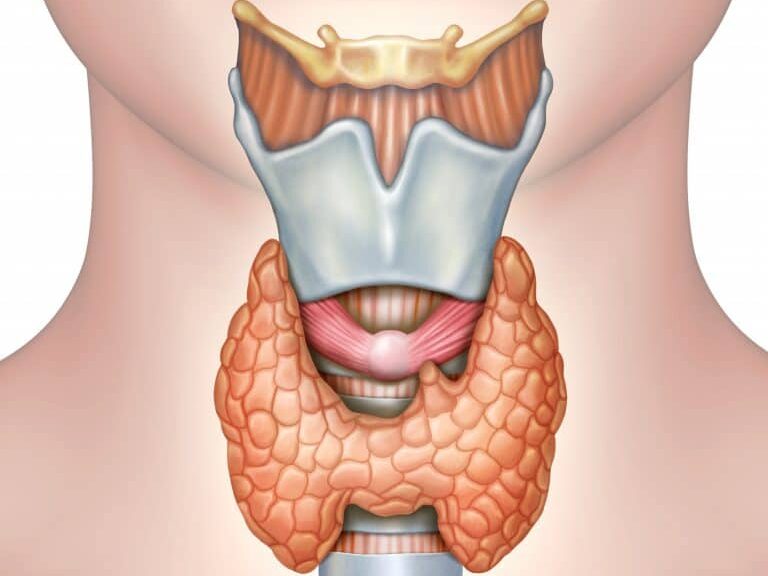
Table of Contents
What Is the Thyroid?
The thyroid gland produces two primary hormones:
- Thyroxine (T4): The main hormone produced by the thyroid, T4 is converted into triiodothyronine (T3) in the body, which is the active form that regulates metabolism.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): T3 is more potent than T4 and is responsible for many metabolic processes.
These hormones play a vital role in:
- Regulating metabolism and energy production
- Controlling heart rate and body temperature
- Supporting brain development and function
- Maintaining healthy skin and hair
Common Thyroid Disorders
Several conditions can affect thyroid function, including:
1. Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid does not produce enough hormones, leading to a slower metabolism. Symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Sensitivity to cold
- Depression
- Dry skin and hair
2. Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the opposite condition, where the thyroid produces excessive hormones, resulting in an increased metabolism. Symptoms may include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Rapid heartbeat
- Increased appetite
- Anxiety and irritability
- Sweating and sensitivity to heat
3. Goiter
A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, which can occur in both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. It may result from iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases, or other factors.
4. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
This autoimmune disorder leads to chronic inflammation of the thyroid, often resulting in hypothyroidism. The immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, affecting its hormone production.
5. Graves’ Disease
Another autoimmune disorder, Graves’ disease causes hyperthyroidism. It results from the immune system stimulating the thyroid to produce excessive hormones.
How to Maintain Thyroid Health
1. Ensure Adequate Iodine Intake
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. Ensure you get enough iodine through dietary sources such as:
- Seafood
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Iodized salt
2. Eat a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support thyroid function. Include foods that are high in:
- Selenium: Found in Brazil nuts, fish, and eggs.
- Zinc: Present in meat, shellfish, legumes, and nuts.
- Iron: Available in red meat, spinach, and beans.

3. Stay Active
Regular exercise promotes overall health and can help maintain healthy thyroid function. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, along with strength training.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively impact thyroid health. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.

5. Get Regular Check-ups
Routine blood tests can help monitor thyroid function, particularly if you have a family history of thyroid disorders or experience symptoms. Early detection is key to effective management.
6. Avoid Environmental Toxins
Limit exposure to chemicals and toxins that may disrupt thyroid function. Common culprits include:
- Heavy metals
- Pesticides
- Plasticizers (like BPA)
7. Consider Supplementation
If you have specific deficiencies, consult with a healthcare provider about possible supplementation. This may include iodine, selenium, or vitamin D, depending on your individual needs.
8. Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is essential for overall health, including hormonal balance. Aim to drink enough water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Proper hydration can enhance metabolic processes and support thyroid function.

9. Regular Check-ups
Regular health check-ups can help monitor thyroid levels and overall health. If you suspect low testosterone or experience symptoms such as fatigue, low libido, or mood changes, consult with a healthcare provider for evaluation and guidance.
Conclusion
Thyroid health is essential for overall well-being, impacting metabolism, energy levels, and various bodily functions. By understanding the role of the thyroid, recognizing common disorders, and implementing strategies to maintain balance, you can support your thyroid health effectively.
If you need any help or have any concerns, contact our healthcare experts at Health Authentica.









