Table of Contents
Introduction
Adnexitis is an inflammation of the female reproductive organs, affecting the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding tissues. It can lead to serious complications if left untreated. In this article, we will dive into the causes of adnexitis, its symptoms, available treatments, and how it can impact your health.
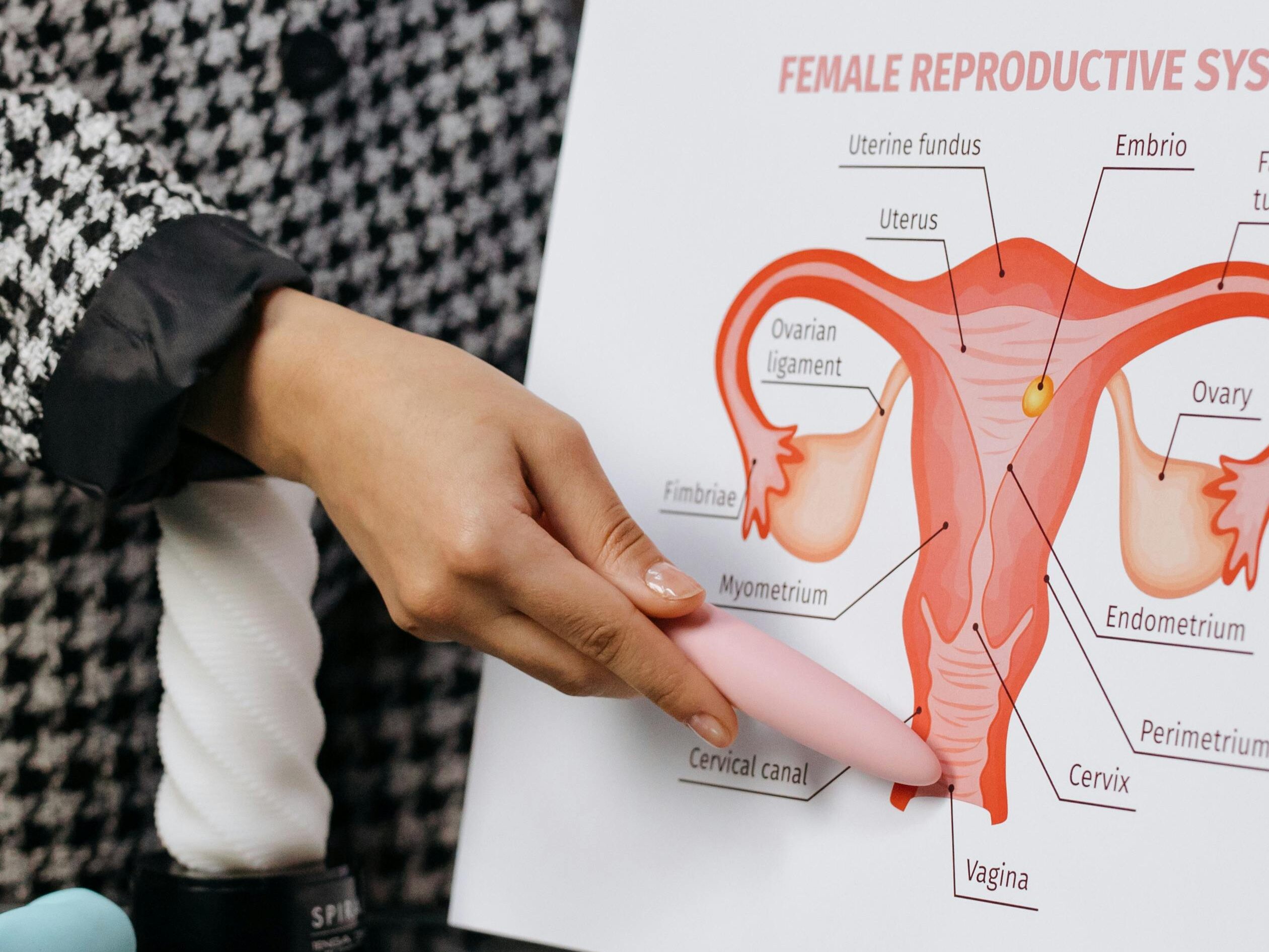
What is Adnexitis?
Adnexitis, also known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) when referring to the broader condition, is a serious infection in the female reproductive organs. It primarily affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes but can also involve the surrounding pelvic tissues. This condition can be caused by bacteria, often as a complication of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Causes and Risk Factors of Adnexitis
Several factors can contribute to the development of adnexitis, and understanding these can help in preventing and treating the condition. The primary causes include:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): These are the leading cause of adnexitis, as the bacteria from infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea can travel to the reproductive organs.
- Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): An imbalance in the vaginal flora can also lead to the development of adnexitis.
- Post-abortion or Post-surgery infections: Any surgical procedure or abortion involving the uterus can increase the risk of infection.
- Multiple sexual partners: This can increase the likelihood of contracting STIs, putting women at higher risk for adnexitis.
While STIs remain the most common cause, other factors like douching or prolonged use of IUDs can increase the chances of developing an infection.
Symptoms of Adnexitis
The symptoms of adnexitis can vary in severity. Some women may experience only mild discomfort, while others may suffer from more severe symptoms. The most common symptoms include:
- Pelvic pain: Often experienced in the lower abdomen or pelvis, sometimes radiating to the lower back.
- Fever: A rise in body temperature can indicate the presence of infection.
- Abnormal vaginal discharge: This discharge may be smelly and greenish or yellow, indicating infection.
- Pain during intercourse: Women may experience discomfort during sexual activity due to inflammation.
- Irregular menstruation: Changes in menstrual cycles may occur in cases of adnexitis.
- Painful urination: In some cases, infection can cause discomfort when urinating.
It’s essential to monitor these symptoms and consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Diagnosis of Adnexitis
If you suspect you have adnexitis, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. A diagnosis typically involves:
- Pelvic exam: To check for tenderness, swelling, or abnormal discharge.
- Ultrasound: An imaging test to view the reproductive organs and check for signs of infection or abscesses.
- Blood tests: To check for elevated white blood cells, indicating an infection.
- Swabs and cultures: These tests can identify the exact bacteria causing the infection.
- Endometrial biopsy: In some cases, doctors may take a small sample of tissue from the uterus to identify bacteria.
Treatment of Adnexitis
The treatment for adnexitis is essential to prevent long-term complications, including infertility or chronic pelvic pain. It generally involves:
- Antibiotics: These are prescribed to treat the infection, and your doctor may recommend a combination of oral and intravenous antibiotics, depending on the severity.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, where the infection has spread, hospitalization and IV antibiotics may be necessary.
- Pain management: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can help manage symptoms.
In cases of severe infection, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove abscesses or damaged tissue. Your doctor will determine the best course of action based on the severity of the infection.
Prevention of Adnexitis
Preventing adnexitis is crucial to maintain reproductive health. Here are a few tips:
- Safe sex practices: Use condoms consistently to prevent STIs.
- Regular checkups: Routine gynecological exams and STI screenings can detect infections early before they develop into more serious conditions.
- Avoid douching: This can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase the risk of infection.
- Limit the number of sexual partners: Fewer partners reduce the risk of STIs.
- Prompt treatment of infections: Always seek treatment for infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea to prevent the spread of bacteria to the reproductive organs.
Conclusion
Adnexitis is a serious condition that requires prompt attention. By recognizing the symptoms early, seeking proper treatment, and practicing preventive measures, you can safeguard your health and prevent long-term complications. If you suspect you have adnexitis or need more information, feel free to contact us at Health Authentica for professional guidance and support.









