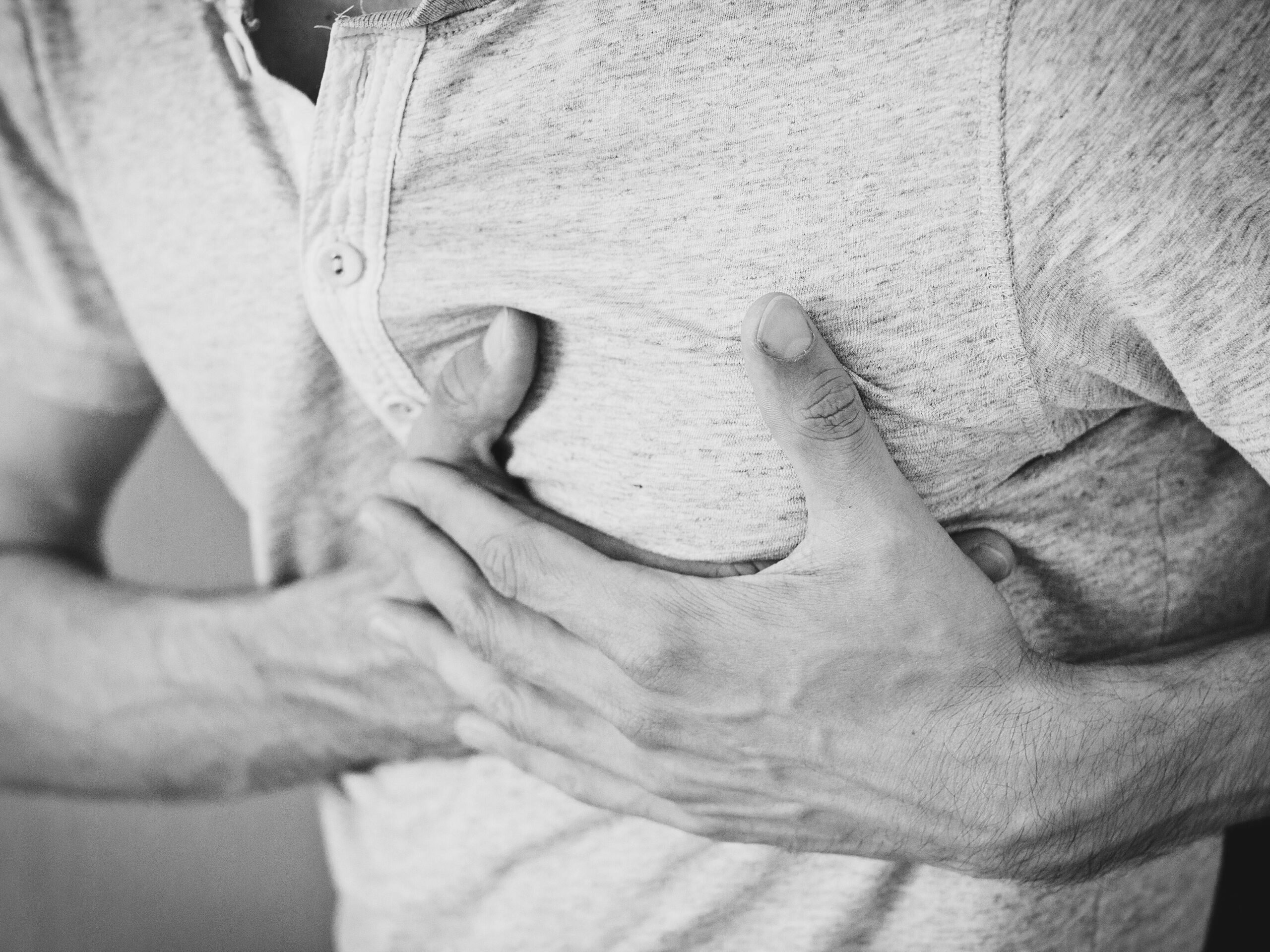
Introduction
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of blood to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. Heart attacks are a leading cause of death worldwide, but the good news is that many are preventable with lifestyle changes and early detection. In this article, we’ll explore what a heart attack is, its causes, symptoms, and seven critical steps you can take to lower your risk and keep your heart healthy.

Table of Contents
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack happens when one or more of the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart, become blocked. This blockage is often caused by a buildup of fatty deposits (plaque), which can rupture and form a clot, cutting off blood flow to the heart. Without adequate blood, the affected part of the heart muscle begins to die, leading to serious health consequences if not treated immediately.
Causes of a Heart Attack
Several factors contribute to the development of heart attacks, including:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the arteries, which narrows and hardens them over time.
- High blood pressure: Puts extra strain on the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of a heart attack.
- High cholesterol: Excess cholesterol can lead to plaque formation, blocking blood flow.
- Smoking: Damages the arteries and lowers oxygen levels in the blood.
- Obesity and physical inactivity: Being overweight or inactive increases the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
The symptoms of a heart attack can vary, but common signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort that lasts more than a few minutes.
- Shortness of breath, even when at rest.
- Pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness, or cold sweats.
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
7 Critical Steps to Prevent a Heart Attack
1. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower your risk of heart disease. Foods high in fiber, like oats and beans, help lower cholesterol levels, while omega-3 fatty acids from fish support heart health. Avoiding trans fats, excess salt, and processed foods can further reduce your risk.
2. Stay Physically Active
Regular exercise strengthens your heart, improves circulation, and helps maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, five days a week. Physical activity also helps manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and stress levels.

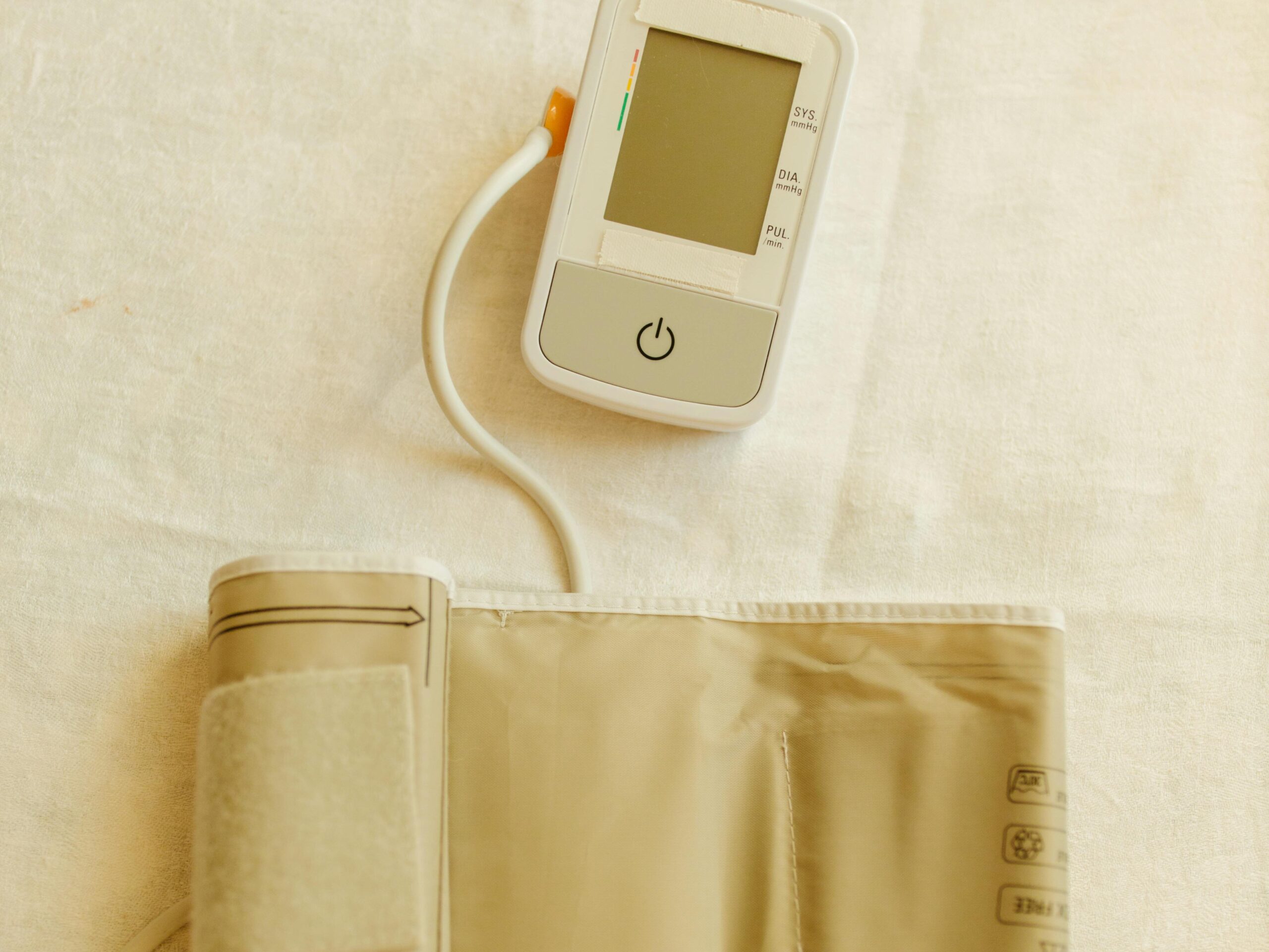
3. Manage Your Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a leading risk factor for heart attacks. Monitoring your blood pressure regularly and following your doctor’s recommendations can help keep it in check. A healthy lifestyle, including reducing salt intake and exercising regularly, can also prevent high blood pressure.
4. Control Cholesterol Levels
High cholesterol levels contribute to the buildup of plaque in your arteries. Regular cholesterol screenings and a heart-healthy diet can help maintain good cholesterol levels. If necessary, your doctor may prescribe medications to lower cholesterol.
5. Quit Smoking
Smoking damages the blood vessels and significantly increases the risk of heart attacks. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to improve heart health. Within a year of quitting, your risk of heart disease drops by half.

6. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases the risk of heart disease. Eating a balanced diet and staying physically active can help you maintain a healthy weight, which reduces your risk of a heart attack.
7. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively affect heart health. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress levels. It’s also important to get adequate sleep and take time for relaxation.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to talk to your doctor about your heart health, especially if you have risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or a family history of heart disease. Regular check-ups, heart screenings, and following your doctor’s advice can help prevent heart attacks and improve your overall health.
Conclusion
Heart attacks can be life-threatening, but many can be prevented by making simple lifestyle changes and managing health conditions like high blood pressure and cholesterol. By following these seven critical steps, you can reduce your risk of heart attacks and keep your heart strong.
If you have concerns about your heart health, contact the experts at Health Authentica for personalized guidance and support!










