Introduction
Amenorrhoea is the absence of menstruation in women of reproductive age. While periods can occasionally be missed due to stress or hormonal changes, consistent absence of menstruation requires attention. Understanding the causes of amenorrhoea and the available treatments is essential for restoring menstrual health and overall well-being.
Table of Contents
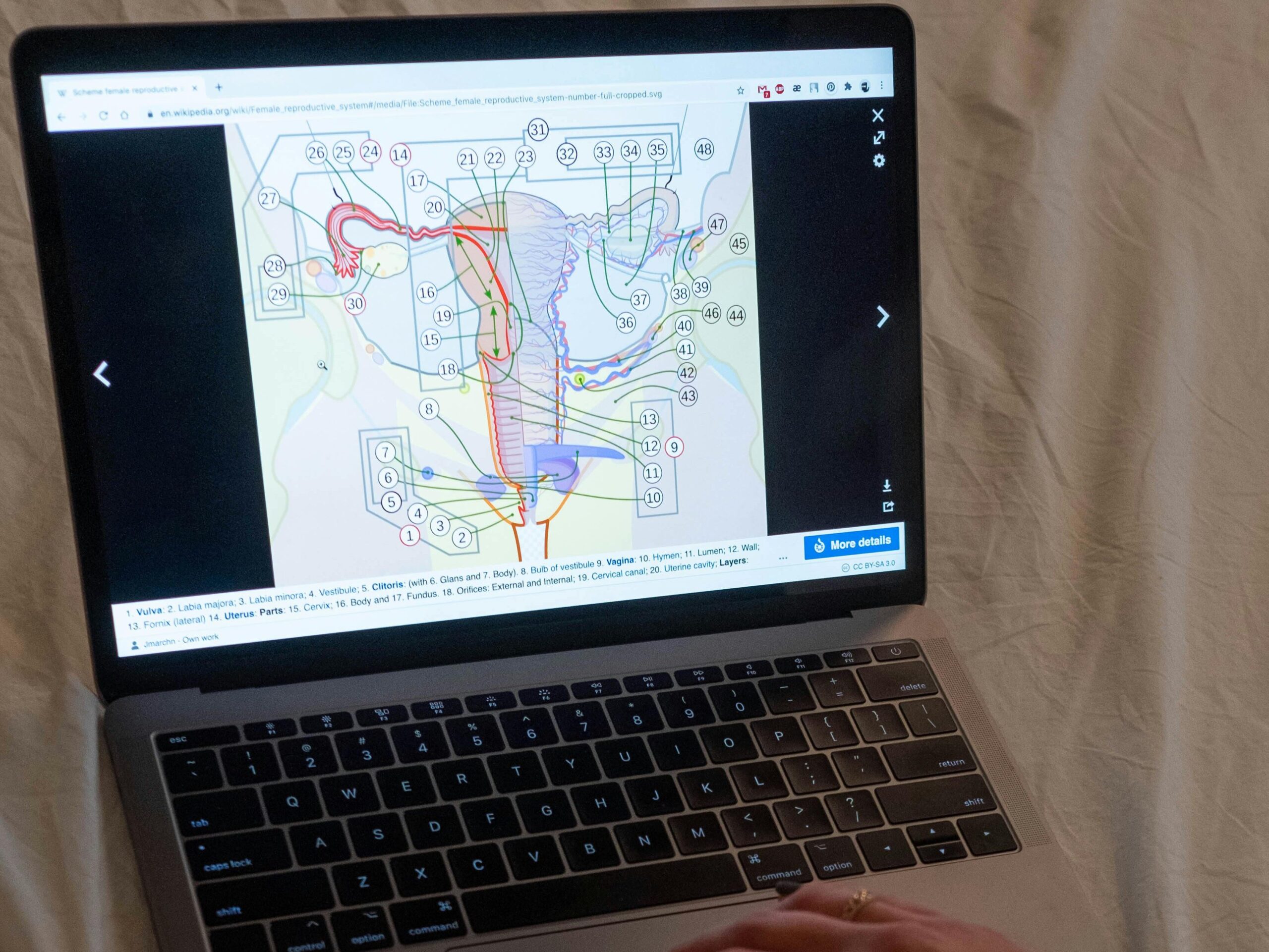
What is Amenorrhoea?
Amenorrhoea is classified into two types: primary and secondary. Primary amenorrhoea occurs when a woman has not had her first period by the age of 16. Secondary amenorrhoea is the more common form, where a woman who previously had regular periods stops menstruating for at least three months.
7 Common Causes of Amenorrhoea
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance, particularly involving estrogen and progesterone, is one of the most common causes of amenorrhoea. Conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or hypothyroidism can disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to missed periods.
2. Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Emotional stress or significant life changes can cause a woman’s body to react in a way that disrupts the menstrual cycle. This includes weight loss, excessive exercise, and even sudden changes in diet. Stress can affect the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that regulates the menstrual cycle.

3. Pregnancy
A missed period is often the first sign of pregnancy. If amenorrhoea occurs and pregnancy is a possibility, it is important to take a test to confirm the condition.
4. Menopause
As women approach menopause, typically between ages 45 and 55, their bodies undergo significant hormonal changes. These changes often lead to irregular periods, eventually resulting in the cessation of menstruation.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune diseases, can also contribute to the development of amenorrhoea. These conditions may affect hormonal balance, ovulation, or the function of the reproductive organs.
6. Medications and Birth Control
Certain medications, particularly those used for chemotherapy, antipsychotic medications, and birth control, may interfere with menstruation. For example, some hormonal contraceptives can cause a temporary stop in periods.

7. Overactive or Underactive Thyroid
The thyroid gland plays a key role in regulating metabolism and menstrual cycles. Both hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can cause amenorrhoea. Treatment for thyroid imbalances often restores menstrual cycles.
Symptoms of Amenorrhoea
In addition to the absence of periods, other symptoms may accompany amenorrhoea depending on the underlying cause:
- Hot flashes or night sweats (especially in the case of menopause)
- Excessive hair growth or acne (common with PCOS)
- Pain during menstruation or heavy bleeding (for some women with hormonal imbalances)
- Changes in weight (either sudden weight loss or weight gain)
How is Amenorrhoea Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider typically diagnoses amenorrhoea through a combination of:
- Physical Exam: A thorough physical examination to check for any physical symptoms such as excessive hair growth or signs of pregnancy.
- Blood Tests: To measure hormone levels and rule out underlying conditions like thyroid disorders or PCOS.
- Ultrasound: A pelvic ultrasound can help detect abnormalities in the reproductive organs, such as cysts or fibroids.
- Pregnancy Test: If pregnancy is a possibility, a test is conducted to rule out this cause.
Treatment Options for Amenorrhoea
1. Hormonal Therapy
For women with hormonal imbalances, birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
Addressing factors such as stress management, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing excessive exercise can help restore menstrual health.
3. Thyroid Treatment
If thyroid dysfunction is the cause, medications such as levothyroxine for hypothyroidism or antithyroid drugs for hyperthyroidism can help normalize menstrual cycles.
4. Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be required to remove any cysts, fibroids, or tumors that may be causing amenorrhoea.
5. Fertility Treatments
For women struggling with infertility due to amenorrhoea, fertility treatments such as ovulation induction may be an option.
Conclusion
Amenorrhoea can result from a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, stress, and medical conditions. Identifying the root cause is key to finding the right treatment and restoring menstrual health. If you experience amenorrhoea or other related symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. If you need more information or help with your health journey, feel free to contact us at Health Authentica.









