Introduction
Urine infections, commonly known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), are a frequent health issue among women. They occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, leading to discomfort and other symptoms. This article will help you understand the causes, symptoms, and ways to prevent urine infections in simple terms.
Table of Contents
Causes of Urine Infections in Women
Urine infections are more common in women due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. Common causes include:
1. Bacterial Invasion: The most common cause is the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli), usually found in the digestive system. It can easily travel from the anus to the urethra.
2. Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection.
3. Poor Hygiene: Improper wiping after using the toilet or not cleaning the genital area thoroughly can lead to the spread of bacteria.
4. Certain Birth Control Methods: Some forms of contraception, like diaphragms, can contribute to urine infections.
5. Menopause: Lower estrogen levels after menopause can cause changes in the urinary tract, increasing the likelihood of infections.

Symptoms of Urine Infections
UTIs can cause various uncomfortable symptoms, including:
1. Painful Urination: A burning sensation while urinating is a common sign of a urine infection.
2. Frequent Urge to Urinate: Feeling the need to urinate often, even if only a small amount comes out, is typical.
3. Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Urine that looks cloudy or has a strong odor may indicate an infection.
4. Lower Abdominal Pain: Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvic area can occur.
5. Blood in Urine: In some cases, a UTI can cause blood to appear in the urine.



4-Key Diagnostic Tests for Urine Infections
To diagnose a urinary tract infection (UTI) accurately, several key tests are performed:
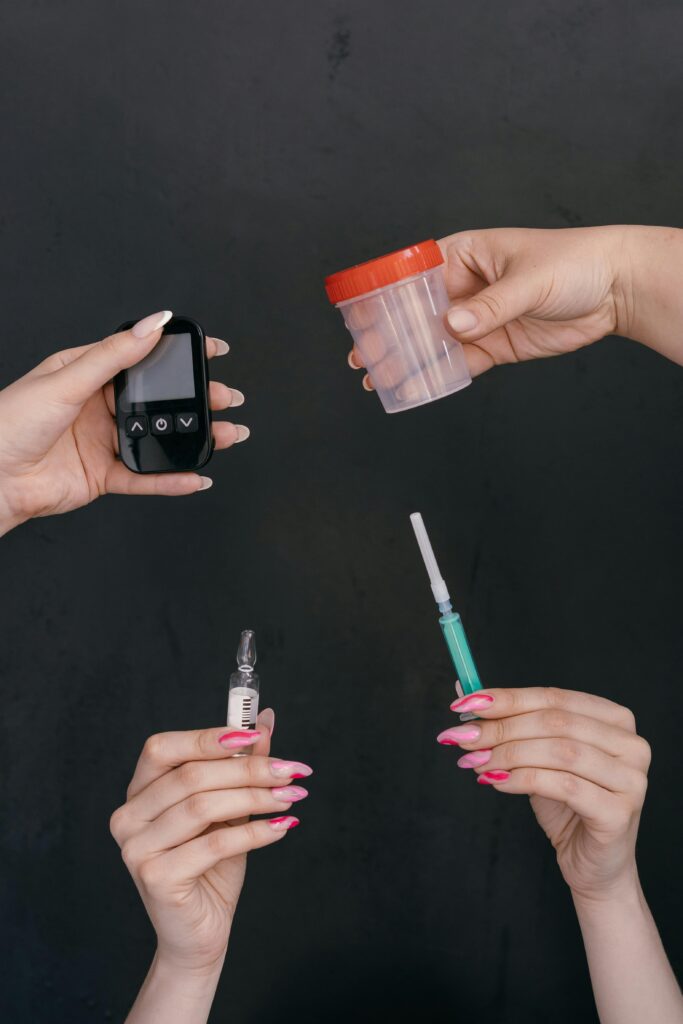
1. Urine Routine and Microscopy:
– Urine Routine: This test involves a basic analysis of a urine sample to check for signs of infection. It examines the presence of bacteria, white blood cells (WBCs), red blood cells (RBCs), and proteins. The presence of WBCs and bacteria in the urine often indicates an infection.
– Urine Microscopy: This involves examining the urine sample under a microscope to identify the presence of bacteria, WBCs, or crystals. It helps confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the infection.

2. Urine Culture:
– This test isolates and identifies the specific bacteria causing the infection. A urine sample is cultured on a growth medium to determine the exact type of bacteria and its antibiotic sensitivity, guiding effective treatment.
3. Complete Blood Count (CBC):
– CBC: This blood test evaluates overall health and identifies signs of infection. It measures various components of the blood, including white blood cells (WBCs), which increase in response to infection. A higher WBC count can indicate an ongoing infection or inflammation.
4. Microscopic Examination of Blood (if needed):
– Microscopic Examination of Blood: This is sometimes done to assess the presence of abnormal cells or other indicators of infection or inflammation, providing additional information about the body’s response to an infection.

Prevention Tips for Urine Infections
Preventing urine infections is possible with some simple lifestyle changes:
1. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
2. Practice Good Hygiene: Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from spreading.
3. Urinate After Intercourse: Emptying your bladder after sex can help remove any bacteria that may have entered the urethra.
4. Avoid Irritants: Avoid using harsh soaps, douches, or feminine hygiene sprays that can irritate the urethra.
5. Wear Comfortable Clothing: Opt for loose-fitting, cotton underwear to keep the area dry and free of bacteria.



Conclusion
Urine infections in women are common but preventable with proper care and hygiene. If you experience symptoms of a UTI, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for treatment. At Health Authentica, we are here to support you with accurate information and guidance to help you maintain your health.










