Introduction
Vaccination is a crucial aspect of pediatric health, helping to protect children from various serious and potentially life-threatening diseases. Understanding the purpose of vaccines and their benefits can help parents make informed decisions about their child’s health.
Table of Contents
What is Vaccination?
Vaccination involves administering a vaccine to stimulate the immune system to protect against specific diseases. A vaccine typically contains weakened or inactivated parts of a microorganism or a blueprint for the immune system to recognize and fight the disease.
Importance of Vaccination
1. Disease Prevention: Vaccines protect children from severe illnesses such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, and more. They help to prevent the spread of contagious diseases within communities.

2. Herd Immunity: High vaccination rates contribute to herd immunity, which protects those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons by reducing the overall prevalence of disease.

3. Long-Term Health Benefits: Vaccination helps prevent long-term complications and serious health issues associated with diseases, such as pneumonia or neurological damage.
Site of Vaccine Injection
Vaccines are administered at specific sites on the body, usually in the arm or thigh, depending on the age and type of vaccine. Common sites include:
1. Intramuscular (IM) Injections: These are given into the muscle, typically in the upper arm for older children or the thigh for infants. IM injections are used for vaccines like DTaP and Hib.
2. Subcutaneous (SC) Injections: Administered just below the skin, often used for vaccines like MMR and varicella. These are typically given in the upper arm or thigh.

3. Oral Vaccines: Some vaccines, such as the rotavirus vaccine, are given orally. This method is convenient and non-invasive.
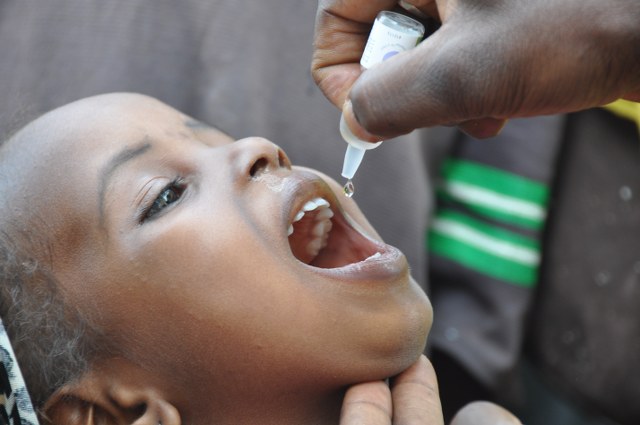
Common Vaccines and Their Benefits
1. MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella): Protects against three viral infections:
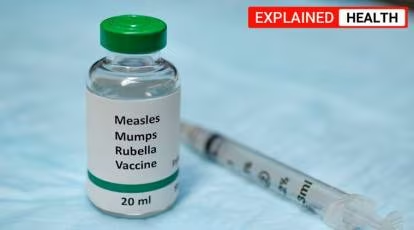
– Measles: Can cause severe complications such as pneumonia, encephalitis, and blindness.
– Mumps: May lead to meningitis, hearing loss, or swelling of the testicles.
– Rubella: Can cause birth defects if a woman is infected during pregnancy.
2. DTaP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis): Provides protection against:
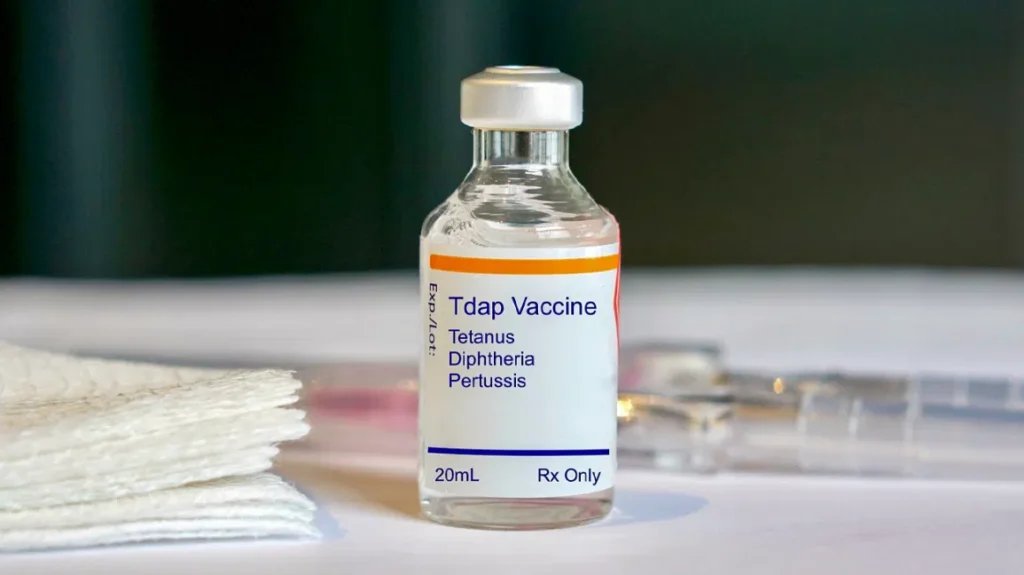
– Diphtheria: A bacterial infection that can cause severe throat swelling and breathing problems.
– Tetanus: A bacterial toxin causing muscle stiffness and spasms.
– Pertussis (Whooping Cough): A highly contagious respiratory disease leading to severe coughing fits.
4. Polio: Prevents poliomyelitis, which can cause paralysis and permanent disability. The vaccine has virtually eliminated polio in many parts of the world.
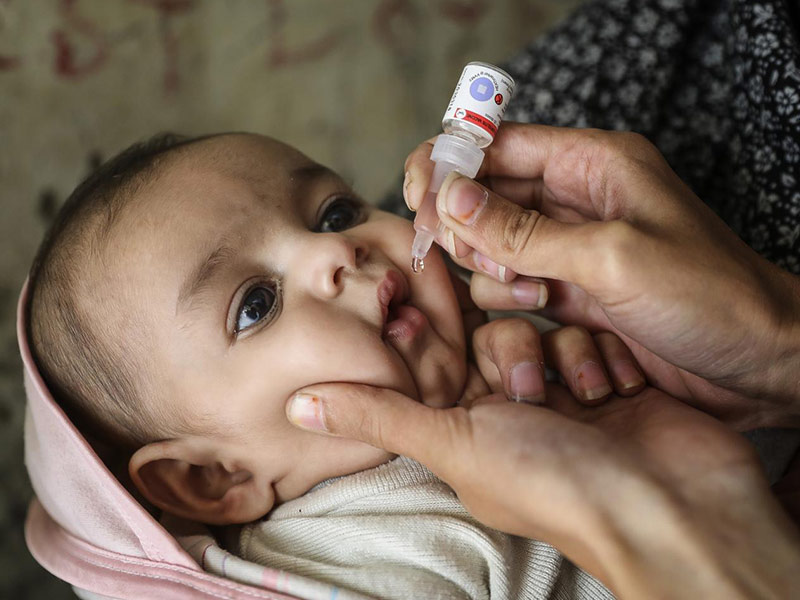
4. Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b): Protects against a bacterial infection that can lead to severe conditions such as:
– Meningitis: Infection of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
– Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs.
– Epiglottitis: Swelling of the epiglottis that can block airflow to the lungs.
5. PCV13 (Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine): Protects against pneumococcal diseases, including:
– Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs that can lead to serious illness or death.
– Meningitis: Infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
– Bacteremia: Presence of bacteria in the blood.
5. Rotavirus: Prevents severe diarrhea and dehydration caused by rotavirus. Rotavirus can lead to hospitalizations due to dehydration and can be particularly severe in young children.
7. Hepatitis B: Provides protection against hepatitis B virus, which can cause:
– Chronic Liver Infection: Can lead to liver damage and increase the risk of liver cancer.
– Liver Cirrhosis: Severe liver damage that affects liver function.
8. Varicella (Chickenpox): Protects against chickenpox, which can cause:
– Severe Itchy Rash: Characterized by red, itchy blisters.
– Complications: Includes skin infections, pneumonia, and in rare cases, brain inflammation.
9. HPV (Human Papillomavirus): Helps prevent HPV infections, which can lead to:
– Cervical Cancer: A type of cancer that affects the cervix.
– Other Cancers: Such as cancers of the throat, vulva, vagina, and anus.
10. Meningococcal (MenACWY): Protects against meningococcal disease, which can cause:
– Meningitis: Serious infection of the brain and spinal cord coverings.
– Meningococcemia: A bloodstream infection that can cause severe illness or death.
Addressing Common Concerns
1. Safety: Vaccines undergo rigorous testing and monitoring to ensure they are safe and effective. Serious side effects are rare.
2. Side Effects: Common side effects, such as mild fever or redness at the injection site, are typically short-lived and less severe compared to the diseases they prevent.
3. Efficacy: Vaccines are highly effective in preventing the targeted diseases and contribute significantly to public health.
Conclusion
Vaccination is a fundamental part of protecting children’s health and ensuring their well-being. By following recommended vaccination schedules, parents can help safeguard their children from serious illnesses and contribute to community health. For specific advice and concerns about vaccines, consult with your healthcare provider at Health Authentica to make the best choices for your child’s health.











2 thoughts on “Vaccination for Children: Essential Information for Parents”